English 

T: +86-0731-85185770
E: enquiry@qilumetal.com
E: enquiry@qilumetal.com
No. 18 Xiangfu Middle Road,Yuhua District, Changsha City

| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |
34Cr4

34Cr4 / 1.7033 is an alloy structural steel classified under European standards EN 10083-3 and EN 10250-3. This steel grade finds extensive application in industrial production, particularly in mechanical manufacturing, automotive components, general engineering structural parts, and transmission components subjected to moderate loads. It corresponds to various grades in international standards, such as 5132 (ASTM A29) in the American standard, SCr435 (JIS G4053) in the Japanese standard, and 35Cr (GB/T 3077) in the Chinese standard.
Through quenching and tempering, 34Cr4 achieves a favorable balance of strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance. This material exhibits excellent hardenability, machinability, and comprehensive mechanical properties, making it commonly used for manufacturing gears, shafts, connecting rods, bolts, and various structural components subjected to dynamic loads.
1: Steel equivalent
Country | USA | Europe | China | Japan |
Standard | ASTM A29 | EN10250-3 | GB/T 3077 | JIS G4053 |
Grade | 5132 | 34Cr4/1.7033 | 35Cr | SCr435 |
2: Chemical composition
Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni |
5132 | 0.30-0.35 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.60-0.80 | 0.035Max | 0.040Max | 0.75-1.00 | / |
34Cr4/1.7033 | 0.30-0.37 | 0.40Max | 0.60-0.90 | 0.035Max | 0.035Max | 0.90-1.20 | / |
35Cr | 0.32-0.39 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.50-0.80 | 0.030Max | 0.030Max | 0.80-1.10 | / |
SCr435 | 0.33-0.38 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.60-0.90 | 0.030Max | 0.030Max | 0.90-1.20 | 0.25Max |
3: Mechanical properties .
Mechanical properties for 34Cr4 quenching and tempering alloy steel according to EN10083-3.
Size range | Tensile strength | Yield strength | Alongation | Area of reduction | Impact value At RT/J |
d≤16 t≤8 | 900-1100Mpa | 700Mpa Min | 12% Min | 35% Min | / |
16<d≤40 8<t≤20 | 800-950Mpa | 590Mpa Min | 14% Min | 40%Min | 40J Min |
40<d≤100 20<t≤60 | 700-850Mpa | 460Mpa Min | 15% Min | 45%Min | 40J Min |
Sampling and preparation of test pieces for 34Cr4 quenching and tempering steel.
1): According to EN10083-1, all samples shall be taken at a distance of 12.5mm below the heat treated surface
2): As stipulated in the contract between buyer and seller.
Mechanical properties for 34Cr4 open die forgings steel according to EN10250-3
Size range | Tensile strength | Yield strength | Alongation | Impact value at RT/J | ||
d≤70 | 700Mpa Min | 460Mpa Min | 15% Min | 40J Min | ||
Sampling and preparation of test pieces for steel forging.
1: According to EN10250-1, all samples shall be taken at a distance of 4/T below the heat treated surface (with a minimum of 20mm and a maximum of 80mm), and t/2 from the end (where t is the equivalent thickness of the thickness of the ruling section of the forging at the time of heat treatment.
2: As stipulated in the contract between buyer and seller.
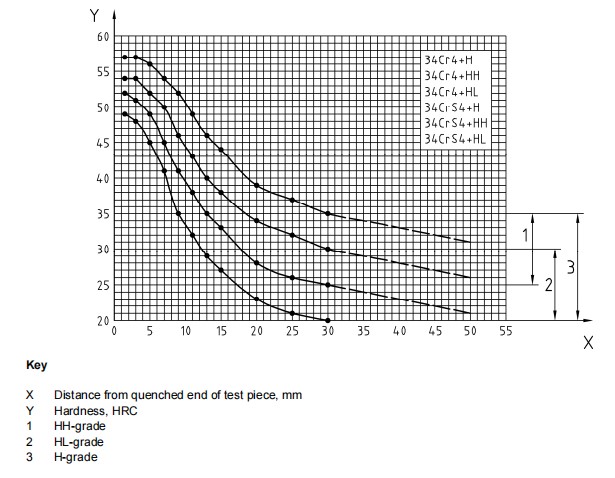
4: Surface hardness and hardenability.
Heat Treatment | Hardness |
| Treated to improve shearability (+S) | HB255Max |
Soft annealed (+A) | HB223Max |
Quenched and tempred (+QT) | HRC28-32(Common Range) |
Where the steel is ordered by using the symbols for normal (+H) or restricted (+HL, +HH) hardenability requirements, the hardenability values should apply below:
Distance in mm from quenched end | ||||||||||||||||
Distance | 1.5 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | |
Hardness In HRC + H | max | 57 | 57 | 56 | 54 | 52 | 49 | 46 | 44 | 39 | 37 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 |
min | 49 | 48 | 45 | 41 | 35 | 32 | 29 | 27 | 23 | 21 | 20 | / | / | / | / | |
Hardness In HRC + HH | max | 57 | 57 | 56 | 54 | 52 | 49 | 46 | 44 | 39 | 37 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 |
min | 52 | 51 | 49 | 45 | 41 | 38 | 35 | 33 | 28 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | |
Hardness In HRC + HL | max | 54 | 54 | 52 | 50 | 46 | 43 | 40 | 38 | 34 | 32 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 |
min | 49 | 48 | 45 | 41 | 35 | 32 | 29 | 27 | 23 | 21 | 20 | / | / | / | / | |
Scatter bands for the Rockwell - C hardness in the end quench hardenability test.

5: Supply size & Tolerance & Stock size
Product type | Size range | Length |
Hot rolled bar | Φ16-Φ300mm | 6000-9000mm |
Hot forged bar | Φ140-Φ800mm | 3000-5800mm |
Hot rolled plate/sheet | T:12-120mm; W:1500-2500mm | 2000-5800mm |
Hot Forged block | T: 80-800mm; W: 100-2500mm | 2000-5800mm |
Surface Finish | Turned | Milled | Grinding(Best) | Polished(Best) | Peeled(Best) | Black Forged | Black Rolled |
Tolerance | +0/+3mm | +0/+3mm | +0/+0.05mm | +0/+0.05mm | +0/+0.1mm | +0/+5mm | +0/+1mm |
Straighness | 1mm/1000mm max. | 3mm/1000mm max. | |||||
Qilu steel stock hot rolled bar and forged bars more than ten thousands tons every month, below our our stock size.
1): Stock diameter for hot rolled bar
16 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 22 | 25 | 28 | 30 | 32 | 35 | 38 | 40 | 42 | 45 | 48 |
50 | 55 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 75 | 80 | 85 | 90 | 95 | 100 | 105 | 110 | 115 | 120 |
125 | 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 | 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 | 250 | 260 |
270 |
Since the stocks change everyday, if you want to know our stock available information, please contact our salesman.
6:Forging processing
Put the 34Cr4 ingot into the furnace and heat to 1150-1200℃
Cooling in the sand after forged
7: Heat treatment
Soft annealed:
Heat 34Cr4 steel to 840-860℃ in the furnace
Soak at this temperature in the furnace
Cooling in the furnace
Normalized:
Heat 34Cr4 steel to 860-900℃ in the furnace
Soak at this temperature in the furnace
Cooling in the air
Quenching and tempering:
Heat 34Cr4 steel to 830-870℃ in the furnace
Soak at this temperature in the furnace
Quench in water or oil
Temper steel at 540-680℃ in the furnace
Take out of 34Cr4 steel from furnace and cool in the air.
Remark: The conditions given above are for guidance, at the temperatures at the lower end of the range are generally applicable to hardening in water and those at the upper end for hardening in oil.
8: Weldability
The weldability of 34Cr4/1.7033 steel is moderate, with carbon content being the key factor affecting weldability. When carbon content exceeds 0.25%, the material's weldability begins to gradually decline. The carbon content range of 34Cr4/1.7033 is 0.30% to 0.37%, which is significantly higher than this critical threshold, thereby increasing its susceptibility to cold cracking during welding to some extent. Additionally, alloying elements such as chromium enhance hardenability, promoting the formation of hard, brittle martensitic structures in the weld heat-affected zone. Therefore, appropriate measures—including preheating, controlled heat input, and post-weld heat treatment—must be implemented during welding to ensure the quality and performance of the welded joint.
9:Application
34Cr4 steel is a chromium alloy structural steel offering a favorable balance between performance and cost. Its primary characteristic is the ability to achieve a good combination of strength, toughness, and wear resistance after quenching and tempering treatment. This makes it a widely used base material across numerous mechanical manufacturing fields. Its main application areas and typical components include:
1. General machinery manufacturing and power transmission systems
Shaft components: Such as various drive shafts, machine tool spindles, pump shafts, gear shafts, automotive half-shafts, etc.
Gears: Used to manufacture medium-sized and medium-load gears, worm gears, and gear rings, commonly found in general-purpose reduction gearboxes, construction machinery transmissions, etc.
Connecting and fastening elements: High-strength bolts, connecting rods, hinge pins, steering tie rods, and other critical connecting components.
2. Automotive Industry
Chassis Components: Steering knuckles, tie rods, stabilizer linkages, torsion bars, etc.
Engine and Transmission Components: Camshafts, crankshaft pulleys, transmission gears and shafts, etc.
3. Construction Machinery and Hydraulic Equipment
Hydraulic components: Widely used in hydraulic piston rods and cylinder barrels, particularly suitable for medium-to-high pressure applications
Construction machinery structural parts: High-wear components like pins, bushings, and spherical plain bearings for excavators and loaders
4. Fixtures and Molds
Mold Manufacturing: Suitable for mold bases and mold plates in large/medium plastic molds, as well as aluminum die-casting mold components with moderate precision requirements
Fixtures & Tools: Machine tool fixtures, chuck components, mandrels, and other specialized tools requiring high rigidity and wear resistance
5. Other General-Purpose Components
Mechanical base components requiring comprehensive performance, such as retaining rings, spring seats, bushings, universal joint forks, etc.

34Cr4 / 1.7033 is an alloy structural steel classified under European standards EN 10083-3 and EN 10250-3. This steel grade finds extensive application in industrial production, particularly in mechanical manufacturing, automotive components, general engineering structural parts, and transmission components subjected to moderate loads. It corresponds to various grades in international standards, such as 5132 (ASTM A29) in the American standard, SCr435 (JIS G4053) in the Japanese standard, and 35Cr (GB/T 3077) in the Chinese standard.
Through quenching and tempering, 34Cr4 achieves a favorable balance of strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance. This material exhibits excellent hardenability, machinability, and comprehensive mechanical properties, making it commonly used for manufacturing gears, shafts, connecting rods, bolts, and various structural components subjected to dynamic loads.
1: Steel equivalent
Country | USA | Europe | China | Japan |
Standard | ASTM A29 | EN10250-3 | GB/T 3077 | JIS G4053 |
Grade | 5132 | 34Cr4/1.7033 | 35Cr | SCr435 |
2: Chemical composition
Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni |
5132 | 0.30-0.35 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.60-0.80 | 0.035Max | 0.040Max | 0.75-1.00 | / |
34Cr4/1.7033 | 0.30-0.37 | 0.40Max | 0.60-0.90 | 0.035Max | 0.035Max | 0.90-1.20 | / |
35Cr | 0.32-0.39 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.50-0.80 | 0.030Max | 0.030Max | 0.80-1.10 | / |
SCr435 | 0.33-0.38 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.60-0.90 | 0.030Max | 0.030Max | 0.90-1.20 | 0.25Max |
3: Mechanical properties .
Mechanical properties for 34Cr4 quenching and tempering alloy steel according to EN10083-3.
Size range | Tensile strength | Yield strength | Alongation | Area of reduction | Impact value At RT/J |
d≤16 t≤8 | 900-1100Mpa | 700Mpa Min | 12% Min | 35% Min | / |
16<d≤40 8<t≤20 | 800-950Mpa | 590Mpa Min | 14% Min | 40%Min | 40J Min |
40<d≤100 20<t≤60 | 700-850Mpa | 460Mpa Min | 15% Min | 45%Min | 40J Min |
Sampling and preparation of test pieces for 34Cr4 quenching and tempering steel.
1): According to EN10083-1, all samples shall be taken at a distance of 12.5mm below the heat treated surface
2): As stipulated in the contract between buyer and seller.
Mechanical properties for 34Cr4 open die forgings steel according to EN10250-3
Size range | Tensile strength | Yield strength | Alongation | Impact value at RT/J | ||
d≤70 | 700Mpa Min | 460Mpa Min | 15% Min | 40J Min | ||
Sampling and preparation of test pieces for steel forging.
1: According to EN10250-1, all samples shall be taken at a distance of 4/T below the heat treated surface (with a minimum of 20mm and a maximum of 80mm), and t/2 from the end (where t is the equivalent thickness of the thickness of the ruling section of the forging at the time of heat treatment.
2: As stipulated in the contract between buyer and seller.
4: Surface hardness and hardenability.
Heat Treatment | Hardness |
| Treated to improve shearability (+S) | HB255Max |
Soft annealed (+A) | HB223Max |
Quenched and tempred (+QT) | HRC28-32(Common Range) |
Where the steel is ordered by using the symbols for normal (+H) or restricted (+HL, +HH) hardenability requirements, the hardenability values should apply below:
Distance in mm from quenched end | ||||||||||||||||
Distance | 1.5 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | |
Hardness In HRC + H | max | 57 | 57 | 56 | 54 | 52 | 49 | 46 | 44 | 39 | 37 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 |
min | 49 | 48 | 45 | 41 | 35 | 32 | 29 | 27 | 23 | 21 | 20 | / | / | / | / | |
Hardness In HRC + HH | max | 57 | 57 | 56 | 54 | 52 | 49 | 46 | 44 | 39 | 37 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 |
min | 52 | 51 | 49 | 45 | 41 | 38 | 35 | 33 | 28 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | |
Hardness In HRC + HL | max | 54 | 54 | 52 | 50 | 46 | 43 | 40 | 38 | 34 | 32 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 |
min | 49 | 48 | 45 | 41 | 35 | 32 | 29 | 27 | 23 | 21 | 20 | / | / | / | / | |
Scatter bands for the Rockwell - C hardness in the end quench hardenability test.


5: Supply size & Tolerance & Stock size
Product type | Size range | Length |
Hot rolled bar | Φ16-Φ300mm | 6000-9000mm |
Hot forged bar | Φ140-Φ800mm | 3000-5800mm |
Hot rolled plate/sheet | T:12-120mm; W:1500-2500mm | 2000-5800mm |
Hot Forged block | T: 80-800mm; W: 100-2500mm | 2000-5800mm |
Surface Finish | Turned | Milled | Grinding(Best) | Polished(Best) | Peeled(Best) | Black Forged | Black Rolled |
Tolerance | +0/+3mm | +0/+3mm | +0/+0.05mm | +0/+0.05mm | +0/+0.1mm | +0/+5mm | +0/+1mm |
Straighness | 1mm/1000mm max. | 3mm/1000mm max. | |||||
Qilu steel stock hot rolled bar and forged bars more than ten thousands tons every month, below our our stock size.
1): Stock diameter for hot rolled bar
16 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 22 | 25 | 28 | 30 | 32 | 35 | 38 | 40 | 42 | 45 | 48 |
50 | 55 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 75 | 80 | 85 | 90 | 95 | 100 | 105 | 110 | 115 | 120 |
125 | 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 | 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 | 250 | 260 |
270 |
Since the stocks change everyday, if you want to know our stock available information, please contact our salesman.
6:Forging processing
Put the 34Cr4 ingot into the furnace and heat to 1150-1200℃
Cooling in the sand after forged
7: Heat treatment
Soft annealed:
Heat 34Cr4 steel to 840-860℃ in the furnace
Soak at this temperature in the furnace
Cooling in the furnace
Normalized:
Heat 34Cr4 steel to 860-900℃ in the furnace
Soak at this temperature in the furnace
Cooling in the air
Quenching and tempering:
Heat 34Cr4 steel to 830-870℃ in the furnace
Soak at this temperature in the furnace
Quench in water or oil
Temper steel at 540-680℃ in the furnace
Take out of 34Cr4 steel from furnace and cool in the air.
Remark: The conditions given above are for guidance, at the temperatures at the lower end of the range are generally applicable to hardening in water and those at the upper end for hardening in oil.
8: Weldability
The weldability of 34Cr4/1.7033 steel is moderate, with carbon content being the key factor affecting weldability. When carbon content exceeds 0.25%, the material's weldability begins to gradually decline. The carbon content range of 34Cr4/1.7033 is 0.30% to 0.37%, which is significantly higher than this critical threshold, thereby increasing its susceptibility to cold cracking during welding to some extent. Additionally, alloying elements such as chromium enhance hardenability, promoting the formation of hard, brittle martensitic structures in the weld heat-affected zone. Therefore, appropriate measures—including preheating, controlled heat input, and post-weld heat treatment—must be implemented during welding to ensure the quality and performance of the welded joint.
9:Application
34Cr4 steel is a chromium alloy structural steel offering a favorable balance between performance and cost. Its primary characteristic is the ability to achieve a good combination of strength, toughness, and wear resistance after quenching and tempering treatment. This makes it a widely used base material across numerous mechanical manufacturing fields. Its main application areas and typical components include:
1. General machinery manufacturing and power transmission systems
Shaft components: Such as various drive shafts, machine tool spindles, pump shafts, gear shafts, automotive half-shafts, etc.
Gears: Used to manufacture medium-sized and medium-load gears, worm gears, and gear rings, commonly found in general-purpose reduction gearboxes, construction machinery transmissions, etc.
Connecting and fastening elements: High-strength bolts, connecting rods, hinge pins, steering tie rods, and other critical connecting components.
2. Automotive Industry
Chassis Components: Steering knuckles, tie rods, stabilizer linkages, torsion bars, etc.
Engine and Transmission Components: Camshafts, crankshaft pulleys, transmission gears and shafts, etc.
3. Construction Machinery and Hydraulic Equipment
Hydraulic components: Widely used in hydraulic piston rods and cylinder barrels, particularly suitable for medium-to-high pressure applications
Construction machinery structural parts: High-wear components like pins, bushings, and spherical plain bearings for excavators and loaders
4. Fixtures and Molds
Mold Manufacturing: Suitable for mold bases and mold plates in large/medium plastic molds, as well as aluminum die-casting mold components with moderate precision requirements
Fixtures & Tools: Machine tool fixtures, chuck components, mandrels, and other specialized tools requiring high rigidity and wear resistance
5. Other General-Purpose Components
Mechanical base components requiring comprehensive performance, such as retaining rings, spring seats, bushings, universal joint forks, etc.