English 

T: +86-0731-85185770
E: enquiry@qilumetal.com
E: enquiry@qilumetal.com
No. 18 Xiangfu Middle Road,Yuhua District, Changsha City

Grade: 30CrNiMo8 1.6580
30CrNiMo8 (1.6580) alloy steel is engineered with a precise chemical composition to deliver superior strength and toughness. Its key elements include Carbon (C: 0.26-0.34%) for core hardness and tensile strength, Chromium (Cr: 1.80-2.20%) for enhanced hardenability and wear resistance, Nickel (Ni: 1.80-2.20%) for exceptional impact toughness, especially in low temperatures, and Molybdenum (Mo: 0.30-0.50%) to improve high-temperature strength and reduce brittleness.
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |
1.6580
Qilu
DIN 30CrNiMo8 (1.6580) is a high-grade quenching and tempering (QT) alloy steel compliant with European standards EN 10083-3 and EN 10250-3, designed for industries demanding exceptional strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance. Unlike standard chromium-molybdenum (Cr-Mo) steels (e.g., 42CrMo4), its optimized composition—including a balanced blend of chromium, nickel, and molybdenum—delivers superior impact resistance and structural stability, even in extreme operating conditions.
A key advantage of this alloy is its global standard equivalence: it aligns with BS 823M30 under the British BS 970 standard, making it a versatile choice for international projects requiring consistent material performance. Hunan Qilu Steel Co., Ltd., a leading Chinese manufacturer, supplies this alloy in a wide range of forms (cold drawn bars, hot rolled bars, forged bars, plates, and blocks) with extensive stock—including monthly inventories of over 10,000 tons of hot rolled and forged bars—to meet urgent production needs.
What sets DIN 30CrNiMo8 apart is its post-quenching-and-tempering mechanical properties: tensile strength reaching up to 1450 Mpa (for small sizes), yield strength as high as 1050 Mpa, and minimum elongation of 9%, ensuring it can withstand heavy loads, dynamic stresses, and harsh environments. These attributes make it a preferred material for critical components in aerospace, defense, energy, and heavy machinery sectors.
The chemical makeup of DIN 30CrNiMo8 is precisely calibrated to enhance strength, toughness, and heat resistance. Each element plays a critical role in optimizing the alloy’s behavior:
Element | Content Range | Key Function |
Carbon (C) | 0.26-0.34% | Enhances hardness and tensile strength; controls martensite formation during quenching to ensure structural stability |
Silicon (Si) | Max 0.40% | Improves oxidation resistance and strengthens the ferrite phase, suitable for high-temperature working environments |
Manganese (Mn) | 0.30-0.60% | Boosts hardenability and reduces brittleness, improving the alloy’s processing performance |
Phosphorus (P) | Max 0.035% | Minimized content to avoid reduced toughness and cold cracking risks |
Sulfur (S) | Max 0.035% | Strictly controlled to prevent hot brittleness during the forging process |
Chromium (Cr) | 1.80-2.20% | Enhances corrosion resistance, hardenability, and wear resistance, extending the service life of components |
Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.30-0.50% | Increases high-temperature strength and reduces temper brittleness, ensuring stable performance under variable temperature conditions |
Nickel (Ni) | 1.80-2.20% | Significantly improves impact toughness and ductility, ideal for low-temperature or dynamic-load applications |
This composition ensures the alloy maintains structural integrity even after rigorous heat treatment and long-term use.
The mechanical performance of DIN 30CrNiMo8 varies with cross-sectional size. Larger sizes require adjusted heat treatment processes to ensure uniform properties.
The following data is based on standard quenching and tempering (QT) processing in accordance with EN 10083-3:
Size range | Tensile strength | Yield strength | Alongation | Area of reduction | Impact value At RT/J |
d≤16 t≤8 | 1250-1450Mpa | 1050Mpa Min | 9% Min | 40% Min | / |
16<d≤40 8<t≤20 | 1250-1450Mpa | 1050Mpa Min | 9% Min | 40%Min | 30J Min |
40<d≤100 20<t≤60 | 1000-1300Mpa | 900Mpa Min | 10% Min | 45%Min | 35J Min |
100<d≤160 60<t≤100 | 1000-1200Mpa | 800Mpa Min | 11% Min | 50%Min | 45J Min |
160<d≤250 100<t≤160 | 900-1100Mpa | 700Mpa Min | 12% Min | 50%Min | 45J Min |
For open-die forgings that comply with EN 10250-3, even when the size reaches 660mm, the tensile strength can still reach a minimum of 800 Mpa, and the impact value is not less than 40 J, which is suitable for manufacturing heavy-duty components such as wind turbine main shafts:
Size range | Tensile strength | Yield strength | Alongation | Impact value at RT/J | ||
L | Tr | L | Tr | |||
d≤160 | 900Mpa Min | 700Mpa Min | 12% Min | 8% Min | 45J Min | 22J Min |
160<d≤330 | 850Mpa Min | 630Mpa Min | 12% Min | 8% Min | 45J Min | 22J Min |
330<d≤660 | 800Mpa Min | 590Mpa Min | 12% Min | 8% Min | 40J Min | 20J Min |
Remark: L= Longitudinal Tr = Transverse
DIN 30CrNiMo8 supports multiple heat treatment processes to meet the hardness requirements of different application scenarios:
Flame/Induction Hardening: Achieves a surface hardness of 53 HRC, suitable for wear-resistant components such as gears and shafts.
Soft Annealing (+A): Maximum hardness of 248 HB, which is convenient for subsequent machining and forming operations.
Quenching & Tempering (+QT): Common hardness range of 28-32 HRC, balancing strength and ductility for most structural applications.
Surface hardness and hardenability
Heat Treatment | Hardness |
Flame or Induction hardening | 53HRC |
Soft annealed (+A) | HB248Max |
Quenched and tempred (+QT) | HRC28-32(Common Range) |
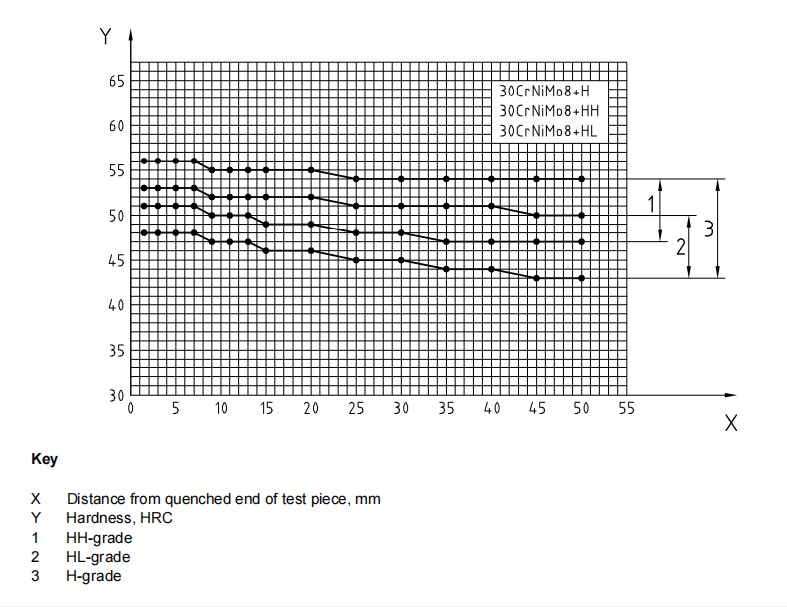
The alloy steel is divided into three hardenability grades (+H, +HH, +HL) to adapt to different quenching needs:
+HH Grade (High Hardenability): Maintains a minimum hardness of 47 HRC at 50mm from the quenched end, suitable for large-sized components.
+HL Grade (Low Hardenability): Ensures hardness consistency, ideal for small and precision parts.
+H Grade (Standard Hardenability): Balances performance and cost, suitable for general-purpose applications.
Distance in mm from quenched end | ||||||||||||||||
Distance | 1.5 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | |
Hardness In HRC + H | max | 56 | 56 | 56 | 56 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 |
min | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 46 | 46 | 45 | 45 | 44 | 44 | 43 | 43 | |
Hardness In HRC + HH | max | 56 | 56 | 56 | 56 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 |
min | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 49 | 49 | 48 | 48 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | |
Hardness In HRC + HL | max | 53 | 53 | 53 | 53 | 52 | 52 | 52 | 52 | 52 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 50 | 50 |
min | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 46 | 46 | 45 | 45 | 44 | 44 | 43 | 43 | |
Scatter bands for the Rockwell - C hardness in the end quench hardenability test.
Hunan Qilu Steel offers a variety of surface finishes to meet the precision requirements of different projects:
Surface Finish | Turned | Milled | Grinding(Best) | Polished(Best) | Peeled(Best) | Black Forged | Black Rolled |
Tolerance | +0/+3mm | +0/+3mm | +0/+0.05mm | +0/+0.05mm | +0/+0.1mm | +0/+5mm | +0/+1mm |
Straighness | 1mm/1000mm max. | 3mm/1000mm max. | |||||
Hunan Qilu Steel provides DIN 30CrNiMo8 in diverse forms and sizes, with tight tolerances to minimize post-processing:
We provide flexible supply specifications to meet diverse customer needs:
Product type | Size range | Length |
Cold drawn bar | Φ3-Φ80mm | 6000-9000mm |
Hot rolled bar | Φ16-Φ310mm | 6000-9000mm |
Hot forged bar | Φ100-Φ1200mm | 3000-5800mm |
Hot rolled plate/sheet | T:3-200mm; W:1500-2500mm | 2000-5800mm |
Hot Forged block | T: 80-800mm; W: 100-2500mm | 2000-5800mm |
Qilu steel stock hot rolled bar and forged bars more than ten thousands tons every month, below our our stock size.
We have plenty of stocks for hot rolled bar, below please check stock size:
8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 16 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 22 | 25 | 30 | 32 | 35 |
38 | 40 | 42 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 75 | 80 | 85 | 90 | 95 | 100 |
105 | 110 | 120 | 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 | 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 |
From dia 8mm to 15mm, they are steel wire, for other diameters, they are steel bar. And if the dia is above 220mm, we have to use hot forged bar, we don't have stock for hot forged bar. Since the stocks change everyday, if you want to know our stock available information, please contact our salesman.
Proper heat treatment and forging are crucial to exerting the full performance potential of DIN 30CrNiMo8. We follow industry best practices to ensure product quality:
Forging Process: Heat the ingot to 1150-1200℃ for full grain refinement, forge at a temperature not lower than 850-900℃ to avoid cracking, and cool in air or sand to eliminate residual stresses.
Soft Annealing: Heat to 680-720℃, keep the temperature uniform, and cool in the furnace to reduce hardness for machining.
Normalizing: Heat to 860-900℃, keep warm, and cool in air to refine the grain structure and improve machinability.
Quenching & Tempering: Heat to 830-860℃ (low temperature for water quenching, high temperature for oil quenching), quench in water or oil, then temper at 540-660℃ and cool in air to adjust hardness and toughness.
These processes ensure consistent mechanical properties and reduce the risk of defects like cracks or warping.
Thanks to its excellent comprehensive performance, DIN 30CrNiMo8 (1.6580) is widely used in high-demand industries that require high strength and toughness:
The exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and impact resistance of DIN 30CrNiMo8 make it ideal for aerospace and defense, where failure is not an option:
Aircraft Components: Landing gear struts, engine shafts, and torsion bars—these parts endure extreme dynamic loads and require fatigue resistance to meet aviation safety standards (e.g., FAA, EASA).
Defense Equipment: Armored vehicle gears, tank drive shafts, and missile launcher structural elements—capable of withstanding ballistic impacts and harsh field conditions.
In sectors where machinery operates under continuous heavy loads, DIN 30CrNiMo8 delivers reliability:
Wind Energy: Main shafts and gearbox components for onshore/offshore wind turbines—resists cyclic stresses from wind turbulence and ensures 20+ years of service life.
Oil & Gas: Drill pipes, lifting hooks, and wellhead components—withstands high pressure, corrosion, and mechanical wear in downhole and offshore environments.
Construction Machinery: Excavator bucket pins, crane boom shafts, and bulldozer transmission gears—handles shock loads and heavy vibrations during construction.
For high-performance and commercial vehicles, the alloy’s toughness and wear resistance are invaluable:
Commercial Vehicles: Truck axle shafts, transmission gears, and clutch components—endure heavy payloads and long-haul use.
Performance Cars: Racing engine crankshafts and differential gears—handles high RPMs and torque without deformation.
The alloy’s machinability and hardness make it suitable for mold and tooling applications:
Heavy-Duty Stamping Molds: Used for stamping thick metal sheets (e.g., automotive body parts)—resists wear from repeated impacts.
Injection Mold Frames: Supports large mold cavities for plastic injection molding—maintains dimensional stability under high temperatures and clamping forces.
With chromium-enhanced corrosion resistance and high strength, DIN 30CrNiMo8 excels in marine settings:
Ship Propulsion Shafts: Transmits engine power to propellers—resists saltwater corrosion and torsional stresses.
Submarine Pressure Housings: Withstands extreme underwater pressure (up to thousands of meters) while maintaining structural integrity.
Offshore Platform Components: Bolts, brackets, and load-bearing structures—endure salt spray, humidity, and wave-induced vibrations.
A1: Three core factors determine performance:
Size: Larger cross-sections have lower tensile strength due to reduced heat treatment penetration. For example, when the diameter exceeds 100mm, the tensile strength drops to 1000-1200 Mpa.
Heat Treatment Parameters: Quenching temperature (830-860℃) and tempering temperature (540-660℃) directly affect hardness. Higher tempering temperature reduces hardness but improves ductility.
Forging Quality: Insufficient forging temperature leads to incomplete grain refinement, and rapid cooling will produce residual stresses, both of which will reduce impact toughness.
A2: This alloy steel has poor weldability, mainly due to two reasons:
Carbon content is about 0.30%, exceeding the 0.25% threshold for good weldability, increasing the risk of cold cracking.
Chromium, nickel, and molybdenum promote hardening in the heat-affected zone (HAZ) during welding.
If welding is necessary, follow these steps:
Preheat the base material to 200-300℃.
Use low-hydrogen electrodes (e.g., E8018-B2).
Perform post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) at 580-620℃ to reduce HAZ hardness.
It is recommended to consult a professional welding engineer for project-specific procedures.
A3: Hunan Qilu Steel implements ISO 9001-certified production processes, with strict quality control in each link:
Raw Material Inspection: Strictly inspect the chemical composition of ingots to ensure compliance with standard requirements.
Process Monitoring: Real-time monitor the temperature and time of forging and heat treatment to avoid process deviations.
Finished Product Testing: Conduct tensile, impact, hardness, and dimensional tests on finished products to ensure that all performance indicators meet customer requirements.
A4: Under normal working conditions and regular maintenance, components made of this alloy steel can have a service life of more than 20 years. For example, wind turbine main shafts made of this material can operate stably for more than 20 years under cyclic stress. The specific service life is related to the working environment and load conditions.
If you need customized solutions or technical support for DIN 30CrNiMo8 (1.6580) alloy steel, please contact Hunan Qilu Steel Co., Ltd. at any time. We are committed to providing high-quality materials and professional services for your project.
DIN 30CrNiMo8 (1.6580) is a high-grade quenching and tempering (QT) alloy steel compliant with European standards EN 10083-3 and EN 10250-3, designed for industries demanding exceptional strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance. Unlike standard chromium-molybdenum (Cr-Mo) steels (e.g., 42CrMo4), its optimized composition—including a balanced blend of chromium, nickel, and molybdenum—delivers superior impact resistance and structural stability, even in extreme operating conditions.
A key advantage of this alloy is its global standard equivalence: it aligns with BS 823M30 under the British BS 970 standard, making it a versatile choice for international projects requiring consistent material performance. Hunan Qilu Steel Co., Ltd., a leading Chinese manufacturer, supplies this alloy in a wide range of forms (cold drawn bars, hot rolled bars, forged bars, plates, and blocks) with extensive stock—including monthly inventories of over 10,000 tons of hot rolled and forged bars—to meet urgent production needs.
What sets DIN 30CrNiMo8 apart is its post-quenching-and-tempering mechanical properties: tensile strength reaching up to 1450 Mpa (for small sizes), yield strength as high as 1050 Mpa, and minimum elongation of 9%, ensuring it can withstand heavy loads, dynamic stresses, and harsh environments. These attributes make it a preferred material for critical components in aerospace, defense, energy, and heavy machinery sectors.
The chemical makeup of DIN 30CrNiMo8 is precisely calibrated to enhance strength, toughness, and heat resistance. Each element plays a critical role in optimizing the alloy’s behavior:
Element | Content Range | Key Function |
Carbon (C) | 0.26-0.34% | Enhances hardness and tensile strength; controls martensite formation during quenching to ensure structural stability |
Silicon (Si) | Max 0.40% | Improves oxidation resistance and strengthens the ferrite phase, suitable for high-temperature working environments |
Manganese (Mn) | 0.30-0.60% | Boosts hardenability and reduces brittleness, improving the alloy’s processing performance |
Phosphorus (P) | Max 0.035% | Minimized content to avoid reduced toughness and cold cracking risks |
Sulfur (S) | Max 0.035% | Strictly controlled to prevent hot brittleness during the forging process |
Chromium (Cr) | 1.80-2.20% | Enhances corrosion resistance, hardenability, and wear resistance, extending the service life of components |
Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.30-0.50% | Increases high-temperature strength and reduces temper brittleness, ensuring stable performance under variable temperature conditions |
Nickel (Ni) | 1.80-2.20% | Significantly improves impact toughness and ductility, ideal for low-temperature or dynamic-load applications |
This composition ensures the alloy maintains structural integrity even after rigorous heat treatment and long-term use.
The mechanical performance of DIN 30CrNiMo8 varies with cross-sectional size. Larger sizes require adjusted heat treatment processes to ensure uniform properties.
The following data is based on standard quenching and tempering (QT) processing in accordance with EN 10083-3:
Size range | Tensile strength | Yield strength | Alongation | Area of reduction | Impact value At RT/J |
d≤16 t≤8 | 1250-1450Mpa | 1050Mpa Min | 9% Min | 40% Min | / |
16<d≤40 8<t≤20 | 1250-1450Mpa | 1050Mpa Min | 9% Min | 40%Min | 30J Min |
40<d≤100 20<t≤60 | 1000-1300Mpa | 900Mpa Min | 10% Min | 45%Min | 35J Min |
100<d≤160 60<t≤100 | 1000-1200Mpa | 800Mpa Min | 11% Min | 50%Min | 45J Min |
160<d≤250 100<t≤160 | 900-1100Mpa | 700Mpa Min | 12% Min | 50%Min | 45J Min |
For open-die forgings that comply with EN 10250-3, even when the size reaches 660mm, the tensile strength can still reach a minimum of 800 Mpa, and the impact value is not less than 40 J, which is suitable for manufacturing heavy-duty components such as wind turbine main shafts:
Size range | Tensile strength | Yield strength | Alongation | Impact value at RT/J | ||
L | Tr | L | Tr | |||
d≤160 | 900Mpa Min | 700Mpa Min | 12% Min | 8% Min | 45J Min | 22J Min |
160<d≤330 | 850Mpa Min | 630Mpa Min | 12% Min | 8% Min | 45J Min | 22J Min |
330<d≤660 | 800Mpa Min | 590Mpa Min | 12% Min | 8% Min | 40J Min | 20J Min |
Remark: L= Longitudinal Tr = Transverse
DIN 30CrNiMo8 supports multiple heat treatment processes to meet the hardness requirements of different application scenarios:
Flame/Induction Hardening: Achieves a surface hardness of 53 HRC, suitable for wear-resistant components such as gears and shafts.
Soft Annealing (+A): Maximum hardness of 248 HB, which is convenient for subsequent machining and forming operations.
Quenching & Tempering (+QT): Common hardness range of 28-32 HRC, balancing strength and ductility for most structural applications.
Surface hardness and hardenability
Heat Treatment | Hardness |
Flame or Induction hardening | 53HRC |
Soft annealed (+A) | HB248Max |
Quenched and tempred (+QT) | HRC28-32(Common Range) |
The alloy steel is divided into three hardenability grades (+H, +HH, +HL) to adapt to different quenching needs:
+HH Grade (High Hardenability): Maintains a minimum hardness of 47 HRC at 50mm from the quenched end, suitable for large-sized components.
+HL Grade (Low Hardenability): Ensures hardness consistency, ideal for small and precision parts.
+H Grade (Standard Hardenability): Balances performance and cost, suitable for general-purpose applications.
Distance in mm from quenched end | ||||||||||||||||
Distance | 1.5 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | |
Hardness In HRC + H | max | 56 | 56 | 56 | 56 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 |
min | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 46 | 46 | 45 | 45 | 44 | 44 | 43 | 43 | |
Hardness In HRC + HH | max | 56 | 56 | 56 | 56 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 |
min | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 49 | 49 | 48 | 48 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | |
Hardness In HRC + HL | max | 53 | 53 | 53 | 53 | 52 | 52 | 52 | 52 | 52 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 50 | 50 |
min | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 46 | 46 | 45 | 45 | 44 | 44 | 43 | 43 | |
Scatter bands for the Rockwell - C hardness in the end quench hardenability test.

Hunan Qilu Steel offers a variety of surface finishes to meet the precision requirements of different projects:
Surface Finish | Turned | Milled | Grinding(Best) | Polished(Best) | Peeled(Best) | Black Forged | Black Rolled |
Tolerance | +0/+3mm | +0/+3mm | +0/+0.05mm | +0/+0.05mm | +0/+0.1mm | +0/+5mm | +0/+1mm |
Straighness | 1mm/1000mm max. | 3mm/1000mm max. | |||||
Hunan Qilu Steel provides DIN 30CrNiMo8 in diverse forms and sizes, with tight tolerances to minimize post-processing:
We provide flexible supply specifications to meet diverse customer needs:
Product type | Size range | Length |
Cold drawn bar | Φ3-Φ80mm | 6000-9000mm |
Hot rolled bar | Φ16-Φ310mm | 6000-9000mm |
Hot forged bar | Φ100-Φ1200mm | 3000-5800mm |
Hot rolled plate/sheet | T:3-200mm; W:1500-2500mm | 2000-5800mm |
Hot Forged block | T: 80-800mm; W: 100-2500mm | 2000-5800mm |
Qilu steel stock hot rolled bar and forged bars more than ten thousands tons every month, below our our stock size.
We have plenty of stocks for hot rolled bar, below please check stock size:
8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 16 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 22 | 25 | 30 | 32 | 35 |
38 | 40 | 42 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 75 | 80 | 85 | 90 | 95 | 100 |
105 | 110 | 120 | 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 | 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 |
From dia 8mm to 15mm, they are steel wire, for other diameters, they are steel bar. And if the dia is above 220mm, we have to use hot forged bar, we don't have stock for hot forged bar. Since the stocks change everyday, if you want to know our stock available information, please contact our salesman.
Proper heat treatment and forging are crucial to exerting the full performance potential of DIN 30CrNiMo8. We follow industry best practices to ensure product quality:
Forging Process: Heat the ingot to 1150-1200℃ for full grain refinement, forge at a temperature not lower than 850-900℃ to avoid cracking, and cool in air or sand to eliminate residual stresses.
Soft Annealing: Heat to 680-720℃, keep the temperature uniform, and cool in the furnace to reduce hardness for machining.
Normalizing: Heat to 860-900℃, keep warm, and cool in air to refine the grain structure and improve machinability.
Quenching & Tempering: Heat to 830-860℃ (low temperature for water quenching, high temperature for oil quenching), quench in water or oil, then temper at 540-660℃ and cool in air to adjust hardness and toughness.
These processes ensure consistent mechanical properties and reduce the risk of defects like cracks or warping.
Thanks to its excellent comprehensive performance, DIN 30CrNiMo8 (1.6580) is widely used in high-demand industries that require high strength and toughness:
The exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and impact resistance of DIN 30CrNiMo8 make it ideal for aerospace and defense, where failure is not an option:
Aircraft Components: Landing gear struts, engine shafts, and torsion bars—these parts endure extreme dynamic loads and require fatigue resistance to meet aviation safety standards (e.g., FAA, EASA).
Defense Equipment: Armored vehicle gears, tank drive shafts, and missile launcher structural elements—capable of withstanding ballistic impacts and harsh field conditions.
In sectors where machinery operates under continuous heavy loads, DIN 30CrNiMo8 delivers reliability:
Wind Energy: Main shafts and gearbox components for onshore/offshore wind turbines—resists cyclic stresses from wind turbulence and ensures 20+ years of service life.
Oil & Gas: Drill pipes, lifting hooks, and wellhead components—withstands high pressure, corrosion, and mechanical wear in downhole and offshore environments.
Construction Machinery: Excavator bucket pins, crane boom shafts, and bulldozer transmission gears—handles shock loads and heavy vibrations during construction.
For high-performance and commercial vehicles, the alloy’s toughness and wear resistance are invaluable:
Commercial Vehicles: Truck axle shafts, transmission gears, and clutch components—endure heavy payloads and long-haul use.
Performance Cars: Racing engine crankshafts and differential gears—handles high RPMs and torque without deformation.
The alloy’s machinability and hardness make it suitable for mold and tooling applications:
Heavy-Duty Stamping Molds: Used for stamping thick metal sheets (e.g., automotive body parts)—resists wear from repeated impacts.
Injection Mold Frames: Supports large mold cavities for plastic injection molding—maintains dimensional stability under high temperatures and clamping forces.
With chromium-enhanced corrosion resistance and high strength, DIN 30CrNiMo8 excels in marine settings:
Ship Propulsion Shafts: Transmits engine power to propellers—resists saltwater corrosion and torsional stresses.
Submarine Pressure Housings: Withstands extreme underwater pressure (up to thousands of meters) while maintaining structural integrity.
Offshore Platform Components: Bolts, brackets, and load-bearing structures—endure salt spray, humidity, and wave-induced vibrations.
A1: Three core factors determine performance:
Size: Larger cross-sections have lower tensile strength due to reduced heat treatment penetration. For example, when the diameter exceeds 100mm, the tensile strength drops to 1000-1200 Mpa.
Heat Treatment Parameters: Quenching temperature (830-860℃) and tempering temperature (540-660℃) directly affect hardness. Higher tempering temperature reduces hardness but improves ductility.
Forging Quality: Insufficient forging temperature leads to incomplete grain refinement, and rapid cooling will produce residual stresses, both of which will reduce impact toughness.
A2: This alloy steel has poor weldability, mainly due to two reasons:
Carbon content is about 0.30%, exceeding the 0.25% threshold for good weldability, increasing the risk of cold cracking.
Chromium, nickel, and molybdenum promote hardening in the heat-affected zone (HAZ) during welding.
If welding is necessary, follow these steps:
Preheat the base material to 200-300℃.
Use low-hydrogen electrodes (e.g., E8018-B2).
Perform post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) at 580-620℃ to reduce HAZ hardness.
It is recommended to consult a professional welding engineer for project-specific procedures.
A3: Hunan Qilu Steel implements ISO 9001-certified production processes, with strict quality control in each link:
Raw Material Inspection: Strictly inspect the chemical composition of ingots to ensure compliance with standard requirements.
Process Monitoring: Real-time monitor the temperature and time of forging and heat treatment to avoid process deviations.
Finished Product Testing: Conduct tensile, impact, hardness, and dimensional tests on finished products to ensure that all performance indicators meet customer requirements.
A4: Under normal working conditions and regular maintenance, components made of this alloy steel can have a service life of more than 20 years. For example, wind turbine main shafts made of this material can operate stably for more than 20 years under cyclic stress. The specific service life is related to the working environment and load conditions.
If you need customized solutions or technical support for DIN 30CrNiMo8 (1.6580) alloy steel, please contact Hunan Qilu Steel Co., Ltd. at any time. We are committed to providing high-quality materials and professional services for your project.